Ensuring cyber resilience is tricky enough at the best of times.
These are far from the best of times.
Against a backdrop of economic decline and geopolitical unrest, cybersecurity threats are growing in frequency and sophistication. 2022 saw a global increase in malware attacks for the first time in more than three years, with 2.3 billion attacks¹. Ransomware, now a billion-dollar industry, is also on the rise.
While headline news stories mainly focus on attacks against large enterprises, it is small and midsize businesses (SMBs) that are most vulnerable. A Ransomware Task Force report cites businesses with fewer than 500 employees were hit by 70% of the attacks in 2021. SMBs are a prime target for cybercriminals because they typically lack sufficient cybersecurity resources, both technology and security expertise, to thwart an attack.

SMB fears becoming reality
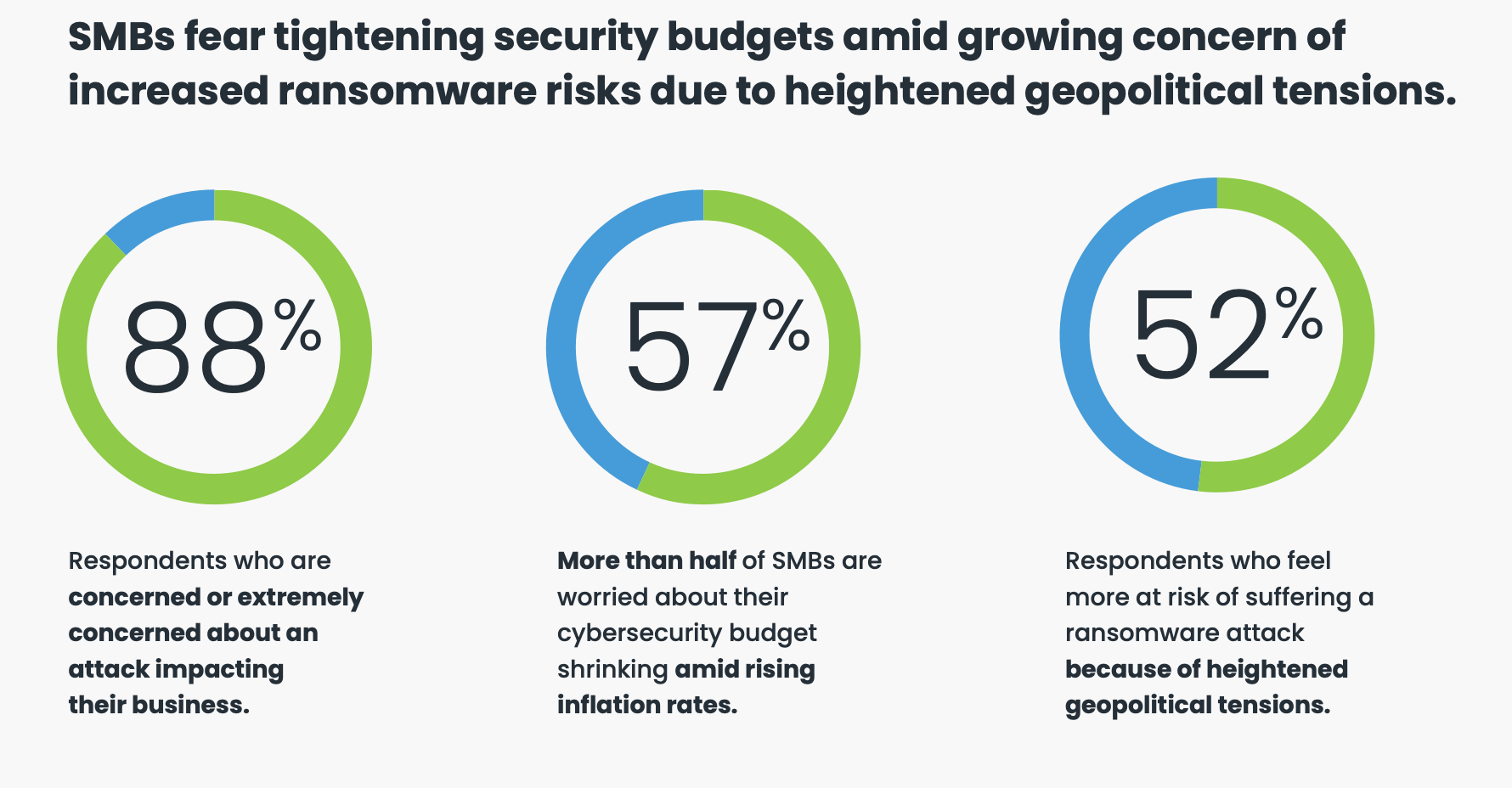
An OpenText Cybersecurity Global SMB Ransomware Survey reveals an overwhelming majority (88%) of SMBs are concerned or extremely concerned about cyber attacks. These concerns have already become a reality for some, with nearly half (46%) of respondents reporting they have experienced a ransomware attack. Meanwhile, 66% of SMBs are not confident or only somewhat confident that they can fend off a ransomware attack. Budget constraints and small security teams were cited as the primary roadblocks.
Adversaries have become increasingly sophisticated and relentless in their efforts to subvert both security controls and humans. Expanding attack vectors make it even more difficult for security teams to stop adversaries which presents a huge risk to businesses of every size. Fortunately, there are some immediate steps organizations can take to keep data secure and protected, even when under a cyber attack.
1. Know your threat vectors: Identify vulnerabilities inside your organization. Pay particular attention to access control which is the biggest business vulnerability for most companies. Limit access to only employees who need it. With controlled access, if an employee falls for a phishing attempt and is compromised, it will not impact the entire company.
2. Train and protect against social engineering: Social engineering tactics like phishing are the number one cause of cybersecurity breaches. When it comes to cybersecurity, your first line of defense, employees, can also be your weakest link. Ensuring employees follow basic online safety protocols and deploying email security are obvious starting points. But as malware attacks grow more sophisticated and more advanced, ongoing education and awareness of new attack vectors and social engineering campaigns are key. Quarterly or monthly phishing simulations are a great way to keep users current and accountable.
3. Safeguard against backup encryption: Have a documented plan to detect, contain and respond to attacks. Planning and practice can greatly minimize the time required for recovery of critical data so businesses can maintain operations. Because even carefully built backup-and-recovery plans can be compromised in an attack, additional safeguards are important. Keep multiple copies of backups in different domains (e.g., local and cloud). Likewise, consider backup solutions that do not allow an attacker to rewrite, encrypt, or modify previous backups. Lastly, keep a history of restored points and backups that cannot be compromised, this will allow access and restore from a good copy of an earlier snapshot.
4. Deploy layered data protection: Because there is no one surefire way to prevent an attack, layered security is key to achieving cyber resilience. Email and endpoint security are great first-line defenses. Even greater protection is achieved when adding recurring security awareness training and DNS protection. Each layer provides a better chance of fending off attacks. In the event a compromise is successful, having tools in place to stop the lateral movement so that businesses can quickly recover from cyberattacks and accidental data loss is essential to achieve cyber resilience.

With security risks escalating worldwide, compromises are inevitable. To ensure cyber resilience, organizations must deploy strong multi-layered security and data protection policies and technologies to prevent, detect and respond, and quickly backup and recover from threats. OpenText Cybersecurity provides a powerhouse SMB platform that helps customers achieve cyber resilience by providing a one stop shop for addressing end-to-end customer priorities: threat prevention, detection and response, recovery, and compliance.
To learn more, go to: https://www.opentext.com/products/security-cloud
___________________________
¹ https://ift.tt/Varn1is
from TechRadar - All the latest technology news https://ift.tt/kSQfcbM




0 Comments